If your business is not prepared, everything could be lost in a cyberattack. Here, CTN compiled statistics to illustrate the reality of an attack and the immediate need to prepare your defenses.
10. Cybersecurity should be top-of-mind for businesses. Everybody is a potential target.

The global information security market is forecasted to reach $170.4 billion in 2022, according to Gartner. And while that number is so large it’s hard to wrap your head around it, here’s another stat that might hit closer to home. According to Cybint, 95% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error, meaning they were likely preventable. Yes, you read that right. Do we have your attention?
9. When a security breach occurs, companies have to hit pause, losing precious time and revenue. This hits small businesses especially hard.

Lost business costs accounts for nearly 40% of the average total cost of a data breach, increasing from $1.42 million in 2019 to $1.52 million in 2020. On average, companies in 2020 required 207 days to identify and 73 days to contain a breach, for a “lifecycle” of 280 days.
(Source: IBM & Ponemon Cost of a Data Breach Report 2020)
8. Depending on the type of information that was compromised, businesses may be on the hook for legal fees.

If a settlement is in the works, a small business could be in limbo for quite some time. It’s common for 3 to 5 years to pass between a breach and a settlement. During that time, the company is paying legal fees, expenses and filing costs—not to mention the cost of the actual settlement.
(Source: Revision Legal)
7. If a company has broken a cybersecurity law, they could also be subject to penalties and fines.

Violating cybersecurity laws is an expensive and disruptive process. Is your company in compliance with current regulations?
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) fines are calculated based on the number of medical records exposed with fines ranging from $50 to $50,000 per record.
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) requires companies offering consumers financial products to explain their information-sharing practices and safeguard sensitive data. Fines can be as high as $100,000 for each violation, and the officers and directors of the organization may be fined up to $10,000 personally.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates the use of encryption and is especially punitive, with fines potentially totaling tens of millions of dollars.
- Being in breach of Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DDS) exposes organizations to minimum fines of $5,000 per month and maximum fines of $100,00 per month.
(Source: CyberInsureOne)
6. If a company is found liable for the leaked information, victims could request compensation.
Perhaps the most sizable example is the Equifax breach that occurred in 2017. Two years later, Equifax agreed to pay nearly $700 million to settle federal and state investigations into how it handled a massive data breach that affected nearly 150 million people.
The settlement included $425 million to directly help consumers affected by the breach. The restitution fund started with $300 million dedicated to consumer compensation, with an additional $125 million if the initial funds ran out.
(Source: CNBC.com)
5. When dealing with a data breach, normal everyday business can fall through the cracks. Lost sales result in lost profits and a very lean bottom line.
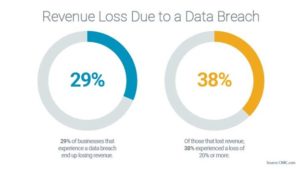
Significant revenue loss as a result of a cybersecurity breach is common. Studies show that 29% of businesses that face a data breach end up losing revenue. Of that lost revenue, 38% experienced a loss of 20% or more.
(Source: The Ame Group)
4. Identifying the breach is one thing, but remediating the situation is an entirely different animal—and the less prepared a company is, the more expensive it will be.
The best defense is often a good offense. The cost of remediation can skyrocket as companies:
- Document the attack
- Quarantine compromised hardware and software
- Contain and eliminate the threat
- Analyze activity logs
- Fix the vulnerability that caused the breach
- Repair or replace infected systems
- Implement security improvements
And ransomware significantly adds to this cost, tacking on an average of nearly $150,000!
(Source: Field Effect)
3. And when operations are subpar, a company will lose customers.

Eighty percent of breached organizations state that personally identifiable information (PII) was compromised during the breach. While the average cost per lost or solen record was $146 across all data breaches, those containing customer PII cost businesses $150 per record—as well as the threat of customers losing faith in the company and turning elsewhere.
(Source: IBM & Ponemon Cost of a Data Breach Report 2020)
2. A breach can damage a company’s reputation—and it can take years to recover.

The biggest cost of a cyberattack is reputation. Deloitte determined that up to 90% of the total costs in a cyberattack occur beneath the surface. Hidden costs, like damaged credibility, can affect a business for years after a breach. What’s more, loss of trust in the business, diminished brand reputation and increased costs concerning debt financing are not covered by insurance.
(Source: Deloitte)
1. In a worst-case scenario, you can lose your entire business.

If everything listed above happens, it can be hard to keep a business afloat. This is especially true for small businesses and why 60% small businesses that are victims of a cyberattack go out of business within six months.
(Source: Fundera)
These statistics tell a story—and it’s a scary one. One (or more) of these situations can easily happen if you aren’t prepared.
